If IE6 (that ancient browser all web developers hate) works, I’m pretty damn sure Chrome 21 will!

It’s time they fixed this. Stop forcing me to launch Firefox!

Technology, law, life, and more.
Computers, hardware, software, and that sort of thing.
If IE6 (that ancient browser all web developers hate) works, I’m pretty damn sure Chrome 21 will!

It’s time they fixed this. Stop forcing me to launch Firefox!
I keep all of my books organized in Librarian Pro by Koingo Software. Admittedly, the Windows port is a sort-of-slow version of the Mac software, but it’s usable and rather pretty.
Along with this, I use a USB barcode scanner to import items by their EAN/UPC barcodes. Librarian Pro connects to Amazon’s APIs and loads book metadata based on that barcode.

After importing a book, I make sure to tag it with a code of my own, specific to my collection. For that, I have these stickers:

And voila, an electronically-catalogued library of books awaits. It’s pretty easy to add location information to the metadata to help look for books, as well as generate HTML pages to show off or sell used books.
I haven’t seen anything published about this yet, but I noticed today that Windows Live Hotmail seems to be authenticating incoming e-mail using DKIM in addition to Sender ID.
In the past, Hotmail has verified the authenticity of incoming e-mail through Microsoft’s proprietary version of Sender Policy Framework called Sender ID. Both of these projects were designed to verify that the computer sending the message, as identified by the originating IP address, is authorized to send e-mail on behalf of the named sender.
A typical SPF policy, specified through a TXT record in DNS, might say
v=spf1 ip4:208.97.132.0/24 -all
This means that only IP addresses in the 208.97.132.1–208.97.132.254 range are allowed to send e-mail on behalf of this domain. (The Sender ID policy would look similar, but starting with spf2.0/pra.)
Hotmail’s policy has been to verify all incoming e-mail using the Sender ID framework. This theoretically reassures users that authenticated e-mail definitely comes from the named sender, reducing the likelihood of header forgery. If an e-mail does not pass Sender ID verification (softfail) and has other signs of being forged, it will likely be classified as junk.
A valid e-mail is marked with these headers:
X-SID-Result: Pass X-AUTH-Result: PASS
If the organization’s policy uses the strictest policy (-all), and the message does not pass Sender ID validation, and the organization has submitted its Sender ID records to Microsoft, invalid e-mail sent to @live.ca and @live.com domains are rejected. As far as I am aware, this protection is not applied to @hotmail.com accounts.
The problem with SPF is that it doesn’t verify much. All it tells us is that an e-mail comes from the right computer—not that an intermediate server hasn’t tampered with it. In addition, SPF only really validates the From: or Sender: headers.
Besides, many large service providers cannot implement a strict SPF/Sender ID policy because users may be sending e-mail through other servers. (For example, I might use my ISP’s SMTP servers to send e-mail from my Windows Live Hotmail address; a strict SPF/Sender ID policy would mark those e-mails as junk.)
DKIM, however, encompasses the contents of the message body, in addition to the headers. It does not necessarily require the e-mail to come from a certain IP address. Using public key cryptography, it allows organizations to take responsibility for sent e-mails by verifying that the e-mail came from an authorized source, similar to the way secure servers connect over TLS/SSL.
Implementing DKIM means that all outgoing e-mails are signed using a private key; the signatures are then checked by compatible software against the public keys published in DNS. Each domain can have multiple DKIM keys, allowing multiple sending systems to sign outgoing e-mails independently.
A sample DKIM signature looks like this:
DKIM-Signature: v=1; a=rsa-sha256; c=relaxed/relaxed;
d=frederickding.com; s=google;
h=domainkey-signature:mime-version:from:date:message-id:subject:to
:content-type;
bh=b3wR4p4G21l92tc0ahioopi7atMwDp2wkaQb/uOL65E=;
b=YJ6nD3Nx5hgwRhYppb/n2g5lQxA5jzFvYEJ0dR4dtkRFv14GVJWStQXwwZryGuujC/
v4ve5ZE3ZAEAtv5hCj99ZLAfR52rskpbitso+106M8uQvryLyuLSnX1mrk6JaDFLMr8V
qHmCEZUF5+cnWEYSwlLo1T8hntgN28hj8OyJY=
DKIM actually requires a lot more work for organizations to implement, as it requires additional DNS lookups and (perhaps) expensive cryptographic calculations. A decade ago, it would have been unfeasible to implement this on an organization as large as Windows Live Hotmail.
Today, the inexpensive cost of processing power makes it possible for Hotmail to validate DKIM. Yahoo! has been doing this since the beginning, as it was the source of this technology. Gmail, too, has been validating DKIM for some time. (Both Yahoo! and Gmail sign outgoing e-mail with DKIM signatures, and Google has made this possible through its Google Apps service for companies as well.)
While Windows Live Hotmail has always validated Sender ID, today I noticed the addition of a new e-mail header:
X-DKIM-Result: Pass
This is good news.
To summarize a post’s worth of babbling, this means that Windows Live Hotmail is taking additional steps to combat e-mail forgery, phishing and spam. A step forward for everybody.
I had been plagued by a nagging question while developing a PHP application: how do I calculate the difference between two timestamps, to check whether the timestamps are within x minutes of each other?
My initial solution wasn’t at all perfect, although it was still better than developing an algorithm from scratch to decipher timestamps into hour/minute/second objects and coding math.
TIMESTAMPDIFF()My first solution was to use a function native to MySQL, TIMESTAMPDIFF(). This function takes in three parameters: the unit of time in which the return value will be, and two datetime expressions.
To query whether a given timestamp was within 15 minutes (either +/-) of the current UTC timestamp, I used this statement:
SELECT ABS(TIMESTAMPDIFF(MINUTE, *********, UTC_TIMESTAMP())) < 15
It worked, but I wasn’t satisfied with having an extra query just to verify a timestamp. Besides, I was concerned about speed; that one query takes about 0.004 seconds to execute, which was too much for me.
Then I discovered the native Date/Time extension, built-in on PHP 5.2 and above.
I’m sure seeing our Spam folder (or Junk, or Junk E-mail, and so on) fill up with useless e-mails is a common occurrence. I’ve learned to ignore it, and I almost never go into it to see if any important e-mails have been mistakenly identified as spam. Fortunately, most of my e-mail accounts don’t get much spam (< 5 a month), perhaps because I switched my main account last year.
Today, I checked my Junk E-mail folder in Outlook to find a phishing e-mail, which, like many others before it, obviously tried to steal login information by posing as the service provider.
Unlike most spam mail about pills, millions of $$$ waiting to be transferred in overseas bank accounts, or pleas for donations for some dying patient, phishing e-mails are often well-crafted and even flawless in grammar and spelling.
In this case, I got an e-mail, purportedly from Blizzard Entertainment, regarding an account lockout. Tech-savvy users immediately look at it with suspicion, but I’m not so sure about the millions of people who have fallen for phishing scams and paid towards a million-dollar industry.
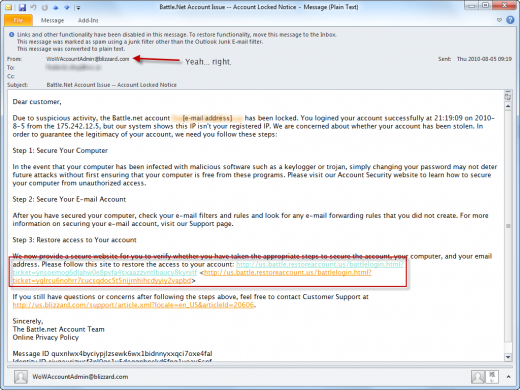
Of course I wouldn’t fall for something like this. First, I don’t play World of Warcraft, nor any video games, really. This makes no sense to me because I don’t have, and never had, a Battle.net account.
Additionally, the headers were revealing:
X-AUTH-Result: NONE ... X-Originating-Email: [xxcipherxx@hotmail.com] Return-Path: xxcipherxx@hotmail.com ... Received: from ri ([222.69.163.30]) by BLU0-SMTP81.blu0.hotmail.com over TLS secured channel with Microsoft SMTPSVC(6.0.3790.4675); ... X-Mailer: Microsoft Outlook Express 6.00.2900.5512 X-MimeOLE: Produced By Microsoft MimeOLE V6.00.2900.5512
This would explain why Outlook, or Hotmail’s SmartScreen junk filtering feature, placed it in the Junk E-mail folder; it originated from a Hotmail user, using Outlook Express, posing as a user @blizzard.com. Most likely it comes from a botnet or otherwise malware-infected PC.
On top of all that, the links don’t point to Battle.net; they link to a domain (restoreaccount.us — visit at your own risk) that is not, at the moment of publishing, recognized by Firefox or Chrome as a phishing site. (I’ve submitted the link to Google’s Safe Browsing system.) This means that most users won’t be automatically protected against losing their accounts to this phishing attack.
I dug deeper to look at the domain registration information for this domain. What if restoreaccount.us was some generic service used by large companies to facilitate user management? (Yeah, right.)
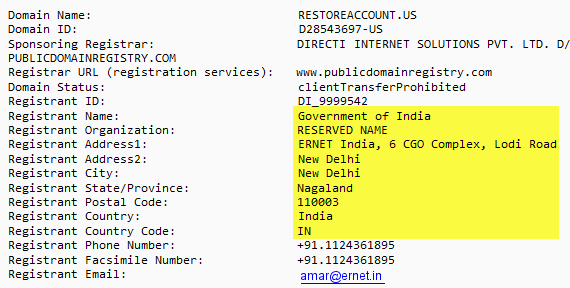
Since phishing is considered fraud, I wasn’t expecting the domain registrant to post his real contact information. To misrepresent oneself, however, on WHOIS contact information is cause for revocation of the domain. While it may be difficult to track down and prosecute fraudsters for phishing (or for impersonating the Government of India), it may be far easier to shut down such operations by disabling their domains through ICANN.
The .us TLD has specific rules restricting registration to permanent residents of the United States, corporations in the United States, and foreign entities pursuing lawful activities in the United States. Supposing the above registrant information to be true (which I doubt very highly), it would not meet the requirements of the .us TLD rules, and could be terminated quickly. If it’s not true, then false registrant information is still a cause for termination.
First, you’re still reading this, so it doesn’t really matter why I decided to write it. Secondly, I wanted to dig deeper and reveal the (poorly) hidden workings of a phishing scam. Thirdly, there are, unfortunately, a lot of people out there who simply don’t understand these attacks and are defenceless against them.
I posted last year about another scam: the Domain Registry of Canada. That has proven to be one of the few posts that attracted a lot of hits from search engines alone, because people are searching about scams (or things they suspect to be scams). (Just to justify that post, I proudly point at the Better Business Bureau’s rating of F for the Domain Registry of Canada.)
In the same sense, I despise phishing and spam. Unsolicited commercial e-mails make up a huge portion of all e-mail traffic — 78%, as a matter of fact. It’d be great if the Internet could be cleaned up, yet at the same time I recognize the difficulties with doing so.
Since government regulation is unlikely to prevent citizens from falling prey to phishing attacks, it’s better to get these things on record and make it possible for people to find out whether they’re being scammed with a quick Google search. (I used such searches recently to avoid: 1) a telemarketing scam, and 2) a career recruitment scam.) There are sites out there dedicated to user-submitted fraud-testimonials.
It doesn’t help that most of the money lost to fraud comes from people who would probably never think to Google the e-mails they receive, or the letters they get. There will always be victims of fraud. We require awareness and education to protect everyone against fraud. I’m simply contributing, like hundreds of thousands of other tech-savvy users, to this struggle.
« Read how it all started in Part 1.
While the initial controversy about the Thesis-not-being-under-GPL issue was focused on themes and derivative works, an unclear area that probably needs to be resolved in court, it seems there is a far sounder reason why Thesis has to be released under the GPL: it blatantly copies WordPress code.
It all started with this tweet by Andy Peatling (@apeatling):
Not a clear GPL violation, because it’s extending WordPress classes, which, in effect, copies WordPress functionality into Thesis.
Andrew Nacin (@nacin) started going through the code of Thesis and started to make some encouraging/discouraging tweets:
I just found a line of code I wrote for #WordPress, but in #thesiswp. Funny, when I wrote it, it was under the GPL. #
And then, an initially uncorroborated claim:
This is really pissing me off. I’m up to a few hundred lines directly lifted from WP. A part of me is crushed. #thesiswp #
And then Drew Blas (@drewblas) did an automated analysis (like I suggested :) ) and found clear evidence of copied WordPress code:

At this point, it seems clear: Thesis isn’t merely building on top of WordPress, it literally incorporates WordPress code through copy-paste.
That makes Chris Pearson liable to fulfill his obligations under the GPL and distribute GPL derivatives under the GPL.
[acm-tag id=”468×60″]
Andrew Nacin eventually found this in Thesis:
* This function is mostly copy pasta from WP (wp-includes/media.php), * but with minor alteration to play more nicely with our styling.
Chris Pearson indicated during his interview that he is fundamentally opposed to the GPL and will absolutely refuse to license Thesis under the GPL. By the end of the dialogue, he was practically saying “sue me”.
Matt Mullenweg responded:
Matt: Are you saying you want to be a test case for the GPL? You want us to sue you? I mean, that would break my heart. I’d rather you be part of the family.
While the themes = derivatives basis might have been shaky for a legal trial, I think the fact that there’s copied code clearly indicates one outcome in the end, in favour of the GPL.
WordPress isn’t the first community to issue the directive that extensions (themes, plugins) are derivatives. Joomla! did so a few years ago (I recall because I used Joomla! before finding WordPress) and Drupal makes it extremely clear.
If this matter can’t be determined by the GPL’s applicability to themes/plugins, maybe WordPress should just re-license, starting with a future version, with GPLv3 and add a specific requirement that themes/plugins are licensed under GPL.